

The maximum is sometimes called the fourth quantile. If you order the numbers in your dataset from lowest to highest, the maximum is the last number.
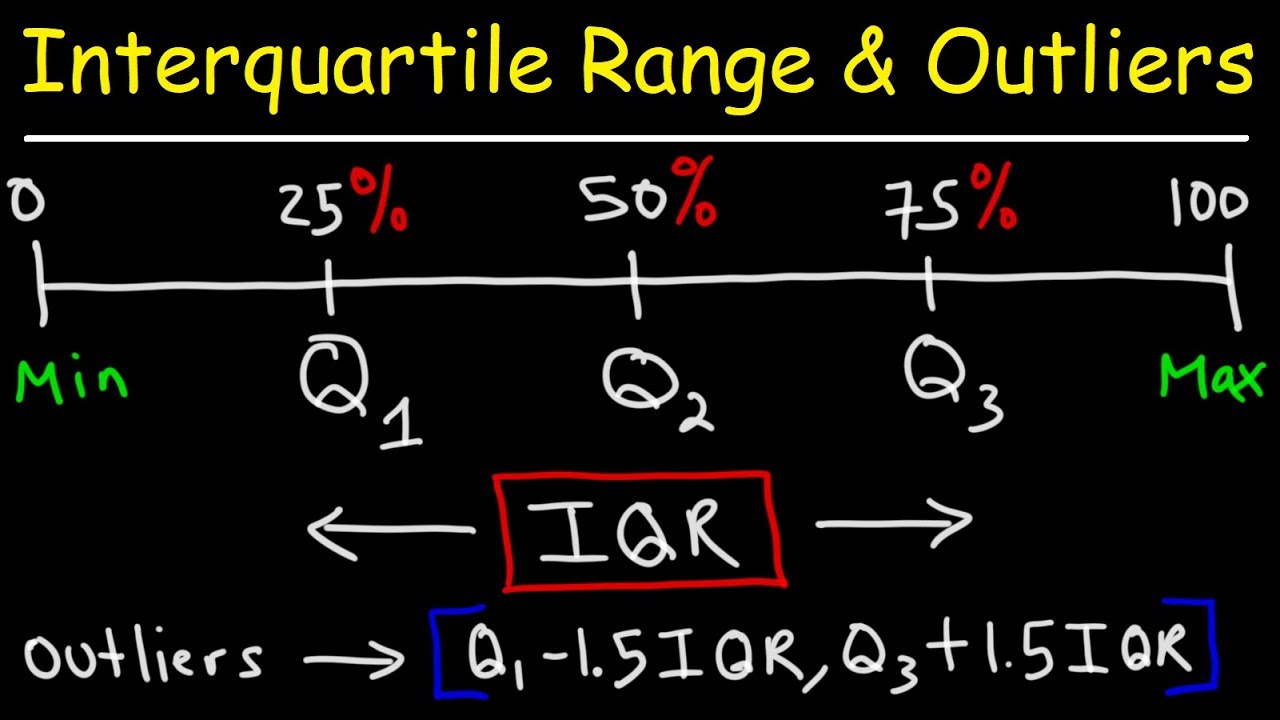
The minimum is sometimes called the zeroth quantile. If you order the numbers in your dataset from lowest to highest, the minimum is the first number. To make a boxplot, you first need to calculate the five-number summary: They’re composed of boxes, which show the quartiles, and whiskers, which show the lowest and highest observations. Q3 = 5 years Visualizing quartiles with boxplotsīoxplots are helpful visual summaries of a dataset. Q2 = 3 years Step 5: Find the third quartile n * (3 / 4) = 14 * (3 / 4) = 10.5ġ0.5 is not an integer, so Q3 is the number at position 11. Q1 = 2 years Step 4: Find the second quartile n * (2 / 4) = 14 * (2 / 4) = 7ħ is an integer, so Q2 is the mean of the numbers at positions 7 and 8. Step 1: Count the number of observations in the dataset n = 2 + 3 + 4 + 1 + 2 + 2 = 14 Step 2: Sort the observations in increasing orderġ, 1, 2, 2, 2, 3, 3, 3, 3, 4, 5, 5, 6, 6 Step 3: Find the first quartile n * (1 / 4) = 14 * (1 / 4) = 3.5ģ.5 is not an integer, so Q1 is the number at position 4. You’re writing a paper about the study and you want to report the quartiles of the children’s ages. Imagine you conducted a small study on language development in children 1–6 years old. Just type “lower quartile x,y,z” to calculate the lower quartile of your data set, or “upper quartile x,y,z” for the upper quartile of your data set. You can switch between the lower and upper quartile in the input field. You can calculate the lower and upper quartile by hand or with the help of our calculator below. There’s no universal agreement on the best way to calculate quartiles. There are multiple methods to calculate the first and third quartiles, and they don’t always give the same answers. The number at this position is the third quartile.
If n * (3 / 4) is not an integer, then round it up. If n * (3 / 4) is an integer, then the third quartile is the mean of the numbers at positions n * (3 / 4) and n * (3 / 4) + 1. The number at this position is the second quartile. If n * (2 / 4) is not an integer, then round it up. If n * (2 / 4) is an integer, the second quartile is the mean of the numbers at positions n * (2 / 4) and n * (2 / 4) + 1. Tip: An integer is a whole number-it can be written without any numbers after the decimal place. The number at this position is the first quartile. If n * (1 / 4) is not an integer, then round it up. If n * (1 / 4) is an integer, then the first quartile is the mean of the numbers at positions n * (1 / 4) and n * (1 / 4) + 1. Sort the observations from smallest to largest. Count the number of observations in the dataset ( n). To find the quartiles of a dataset or sample, follow the step-by-step guide below. In a probability distribution, the quartiles divide the distribution’s range into four intervals with equal probability. In a sample or dataset, the quartiles divide the data into four groups with equal numbers of observations. The third quartile (Q3, or the upper quartile) is the 75th percentile, meaning that 75% of the data falls below the third quartile.īy splitting the data at the 25th, 50th, and 75th percentiles, the quartiles divide the data into four equal parts. The second quartile (Q2, or the median) is the 50th percentile, meaning that 50% of the data falls below the second quartile. The first quartile (Q1, or the lowest quartile) is the 25th percentile, meaning that 25% of the data falls below the first quartile. In general terms, k% of the data falls below the kth percentile. A percentile is a value with a certain percentage of the data falling below it. They summarize the central tendency and variability of a dataset or distribution. 
Quartiles are a set of descriptive statistics.
Frequently asked questions about quartiles and quantiles. The interquartile range of the weights of these babies is 0.9 kg. \ħ babies are weighed and weigh the following amounts:Ģ.5 kg, 3.1 kg, 3.4 kg, 3.5 kg, 3.5 kg, 4 kg, 4.1 kgįind the range of the weights of the babies. The range of a set of numbers is the largest value, subtract the smallest value. If the range is small, the data is closer together or more consistent. 
The bigger the range, the more spread out the data. In statistics, a range shows how spread a set of data is.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
